ISCC Members’ Networking Lunch
February 16, 2024
8th Annual Charity Ski Race
April 7, 2024
One of the important issues in today’s world is the issue of human health and well-being. Undoubtedly, the physical and mental health of individuals in society is of great importance. Ensuring the health of all segments of society is one of the fundamental issues of any country, which should be considered from the three dimensions of physical, mental, and social aspects. Mental health is not only the goal of any society but also considered as a criterion for individual well-being. This term has multiple meanings that vary from one society to another, from one culture to another, and from one individual to another.
For this reason, in psychology, there are different patterns and perspectives on mental health. Mental health and its components are among the important subjects that are influenced by various psychological and environmental variables, and industries and organizations of various professions have paid special attention to it in order to improve organizational productivity (Dehdari & colleagues, 2018). Destructive behaviors in organizations can affect the physical, mental health, and work performance of individuals (Emrallahibeyki, Arami Ardakani, 2020).
In today’s work environments with high pressure and demands, employers must prioritize mental health to ensure the well-being and productivity of employees. This article examines the role of mental health in the workplace and provides strategies for creating a supportive environment that promotes mental health.
Work is one of the fundamental factors in the progress of human society, social life, and consequently, human life. From the moment a person steps into the realm of nature, they have the right to full use of natural resources, and in the pursuit of using these resources, work and activity become the main stimulus for production (Yaghoubpour & Fatemi Nezhad, 2017). On the other hand, favorable working conditions have a direct impact on improving mental health. Mental health in the workplace requires increasing job compatibility, job motivation, job success, job commitment, and reducing job stress, job burnout, and job conflicts (Law, 2010), and it is not a unitary and independent concept but is influenced by various psychological and environmental variables (Jalalian, Garami Pour & Barjalali, 2016).
Studies within the country show that one of the most influential factors on mental health is employment and its quality (Besharat, 2009). Various definitions of mental health have been presented so far, such as the absence of illness, emotional balance, social adaptation, comfort and well-being, personal integrity, self-awareness, and environment. One of the widely accepted definitions of mental health states that mentally healthy individuals are those who are in harmony with themselves and their environment; they construct themselves according to their cultural and social requirements, and if they have a medical disorder, this problem does not lead to the destruction of their reasoning, mental ability, and personal and social adaptation power (Sadock & Sadock, 2016).
Since human personality is formed by cognitive, physical, and social dimensions, the health of their mind and body is at the forefront of their holistic and harmonious growth in all dimensions (Wood, 2016). The prevalence of physical and mental illnesses is increasing in most developed and developing countries, and today many employees are facing mental health problems in the workplace and in life (Kalaf, Rubin, Malachowski, & Kirch, 2016).
Mental health issues in the workplace have raised concerns from both economic and humanitarian perspectives. The costs of mental illnesses for businesses include decreased productivity, absenteeism, and the like (Lim, Jacobs, Ohinmaa, Schopflocher, & Dewa, 2008). For this reason, interest and attention to mental health in the workplace have become widespread. The presence of organizational mental health is one of the most important indicators of a healthy organization, ensuring not only physical health but also the mental health of employees. People work for various reasons such as economic, familial, and social reasons (Owen & Sivertsen, 2014). Therefore, they have the right to have a healthy and safe environment, and mental health is a state in which an individual understands their abilities, can cope with everyday life pressures, increase their productivity, work more effectively, and help their community (Ding, Berry, & Aubrey, 2015).

Organizations that have high levels of mental health are organizations where growth, development, and advancement are easy and there is a willingness to achieve goals quickly. By utilizing available resources, potential talents of members can be transformed at the right time and with minimal costs to increase organizational productivity and create sustainable development (Mahdad, Dehghan, Golparvar, & Shojai, 2012).
Mental health is considered one of the basic needs of humans and is considered the most important aspect for improving the quality of life (World Health Organization, 2009). Mental health has been defined in various ways by researchers from different cultures, and considering the differences between cultures, it is not possible to provide a comprehensive definition of mental health; however, there is a consensus that mental health is more than just the absence of mental disorders and what is clear is that maintaining mental health, like physical health, is important (Abbasi-Zadeh et al., 2003). The health of employees, both physically and mentally, has a significant impact on their effectiveness and efficiency. Often, this issue is neglected because it is intangible and difficult to measure, while its impact on an individual’s efficiency is much greater than their physical health. Therefore, mental health problems are becoming an increasing concern for organizations and societies (Bavorsad et al., 2014). Therefore, attention to the mental health of employees and the factors affecting it can be a key to solving many management problems and concerns (Ebrahimi et al., 2013).
The impact of mental health on productivity
Issues related to mental health can have a significant impact on employee productivity. According to the World Health Organization report, depression and anxiety disorders annually cost the global economy one trillion dollars in lost productivity. Employees dealing with mental health issues may struggle with focus, decision-making, and task completion. They may also take more sick leave due to illness or job burnout. Therefore, addressing mental health in the workplace is not only a compassionate issue but also makes good business sense (World Health Organization, 2019).
Creating a supportive work environment

Employers play a crucial role in creating a supportive work environment that enhances mental well-being. This can be achieved through several accessible strategies, including:
- Increasing awareness: Employers can increase awareness about mental health by providing information and resources to employees. This can include workshops, seminars, and access to mental health professionals.
- Encouraging open communication: Establishing a culture of open communication where employees feel comfortable discussing their mental health concerns. Employers can provide confidential channels for employees to seek support and guidance.
- Providing flexible work arrangements: Flexible work arrangements, such as remote work options or flexible hours, can help employees effectively manage their mental health. This can reduce stress and improve work-life balance.
- Offering mental health benefits: Employers can offer mental health benefits as part of their employee assistance programs. This can include access to counseling services, therapy sessions, and mental health support hotlines.
- Promoting work-life balance: Encouraging a healthy balance between work and life can help prevent job burnout and reduce stress among employees. This can be achieved through policies that promote regular breaks, paid time off, and limits on overtime (Workplace Mental Health Center, 2021).
The field of mental health is a branch of psychology that focuses on preventing mental disorders and maintaining optimal ways of living and emotional well-being (Shabiri, 1392). The World Health Organization (2003) defines mental health in concepts such as mental well-being, perceived self-efficacy, autonomy, competence, and the ability to realize one’s mental and emotional potentials. Some theorists such as Allport, Fromm, Rogers, Maslow, Erikson, Jung, and Frankl focus on the healthy nature of the human being. These psychologists strive to enrich the human personality and provide unique feedback on psychological development and human perfection. On the other hand, another group connects mental health to abnormal behavior or moderate mental illness in defining cognitive mental health and concludes that cognitive mental health is actually equivalent to the absence of mental illness. It is obvious that individuals’ health is not limited to physical health alone; it also encompasses their psychological and social aspects of life (Mohammadi, 1385). In fact, cognitive mental health refers to a state where individuals understand their abilities, are efficient and more productive, can cope with natural life stresses, and contribute to their communities (Friedli, 2009). According to Riff (1989), cognitive mental health has various aspects as shown in the figure below.
Research has shown that factors contributing to workplace psychological anxiety include job ins
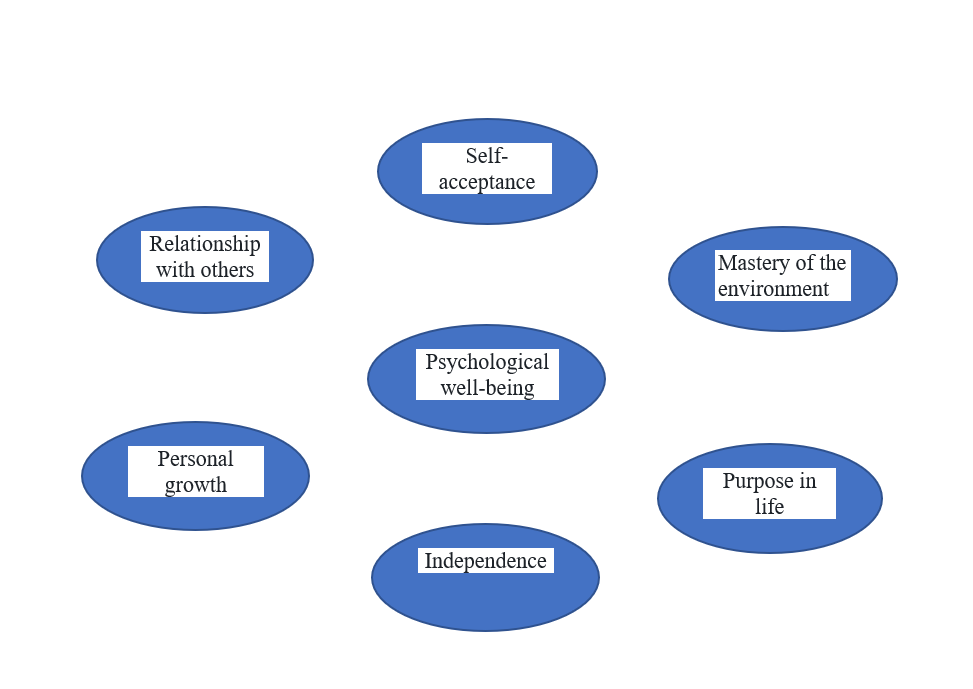
ecurity and lack of social support (Marchand & Blanc, 2010). Factors that promote mental health in the workplace include control opportunities, skill utilization opportunities, externally set goals, environmental diversity, environmental clarity, access to money, physical security, opportunities for social contact, and valuable social status (Ware, 1989; as cited in Mahdadi et al., 2012).
Studies indicate that the process of improving mental health in the workplace is not only important for enhancing the health of employees but also for improving productivity and reducing financial costs such as absenteeism and other illness-related expenses (Kalaf et al., 2016).
A healthy workplace can contribute to both mental and physical well-being (Mac, 2013). Healthy workplaces include health promotion activities, employee assistance programs, flexible benefits and working conditions, fair treatment of employees, employee advancement, health and safety, and ultimately, stress prevention (Gloovi & Day, 2005). When an employee’s mental health is valuable to the organization, they can use work as a source to protect themselves from the effects of non-productive stressors and develop self-reliance, self-confidence, and hope, which helps them in promoting mental health (Luthans, 2002).
Unhealthy workplaces may lead to mental weakness and physical health problems (Gloovi & Day, 2005). Research has shown that psychological factors in the workplace include psychological demands, low control, job insecurity, and lack of social support (Marchand & Blanc, 2010). Additionally, work-related stressors such as workload, roles, job concerns, programs, interpersonal relationships, job content, and job control impact mental health (Gloovi & Day, 2005) and business outcomes (Harter, Schmidt, & Hayes, 2002).
 Job satisfaction leads individuals to perform their responsibilities with enthusiasm and enjoy their work. This results in a sense of calmness and distance from stress and agitation in the autonomic nervous system, leading to lower job-related stress levels and contributing to mental well-being. Conversely, individuals dissatisfied with their jobs experience psychological stress and tension, ultimately leading to anxiety and psychosomatic illnesses. Employees in organizations may be exposed to various social and psychological risks depending on the nature and characteristics of their job, such as spatial and temporal dimensions, environmental and physical factors, job difficulty, as well as other influential factors like individual and organizational factors. It is evident that mental and physical health is a universal need for all individuals, and we all strive to find healthy personalities in human life to establish healthy relationships. Job satisfaction can contribute to the mental well-being of employees and is a crucial factor in enhancing productivity and fostering a positive attitude towards work. Job satisfaction is a complex and multidimensional concept that is related to psychological, social, and physical factors.
Job satisfaction leads individuals to perform their responsibilities with enthusiasm and enjoy their work. This results in a sense of calmness and distance from stress and agitation in the autonomic nervous system, leading to lower job-related stress levels and contributing to mental well-being. Conversely, individuals dissatisfied with their jobs experience psychological stress and tension, ultimately leading to anxiety and psychosomatic illnesses. Employees in organizations may be exposed to various social and psychological risks depending on the nature and characteristics of their job, such as spatial and temporal dimensions, environmental and physical factors, job difficulty, as well as other influential factors like individual and organizational factors. It is evident that mental and physical health is a universal need for all individuals, and we all strive to find healthy personalities in human life to establish healthy relationships. Job satisfaction can contribute to the mental well-being of employees and is a crucial factor in enhancing productivity and fostering a positive attitude towards work. Job satisfaction is a complex and multidimensional concept that is related to psychological, social, and physical factors.
A single factor alone does not lead to job satisfaction, and a specific combination of various factors causes an individual to feel satisfied with their job at a particular moment in time and to say that they are happy with their job and enjoy it. Depending on various factors such as income level, social value of the job, working conditions, and employment at different times, individuals feel satisfied with their job in different ways. Feeling satisfied is the ideal of every institution and organization, and large and extensive companies such as oil companies are not exempt from this issue and even consider it more important to improve organizational efficiency. Therefore, it is clear that employees who are satisfied with their job in various ways will have high levels of mental, physical, emotional, and social well-being. This is why a satisfied employee truly loves their job, has positive feelings about their work, values their job highly, has positive emotions and feelings about their job, and this job satisfaction has the potential to impact a wide range of behaviors in the organization and contribute to their mental health and well-being.
On the other hand, employees who have job satisfaction are satisfied with their level of pay and benefits, have job security that reassures them, are satisfied with the way promotions and advancements are handled and the timing of them, feel comfortable with their colleagues and supervisors or managers in their area, are happy with the organization’s policies, and their working conditions. All of these factors can contribute to their overall satisfaction and the resulting satisfaction can lead to their well-being. Health, which comes with inner peace or the power of living peacefully, self-awareness, decision-making power in crises, and successful coping with mental pressures. It is obvious that a satisfied employee, while emotionally and behaviorally adapting, has a relative stability and moderation and enjoys life and being with others, is satisfied with work and life, and makes good use of their time. Such a person can love, accept love, accept truths, align themselves with them, and reconcile with society. Kahh and Heoody (2011) showed in a study that mental health is significantly related to the components of “overall job satisfaction, satisfaction with cultural environment, and satisfaction with cultural behavior”, and individuals who expressed higher satisfaction also had better mental health.
They also showed that individuals’ income does not affect their mental health, but job satisfaction is a significant factor in influencing mental health. Pirbalouti and colleagues (2014) also demonstrated in a study that there is a positive and meaningful relationship between job satisfaction and employees’ mental health, and job satisfaction significantly predicts mental health. The guide for individuals with mental health is their present moment, goals, and expectations for the future. These fundamental aspects and roots of human personality form his measured and conscious purposes, hopes, and desires. These goals actually motivate a healthy personality and are the best guide to understanding human current behavior. It is also quite clear in explaining this finding that healthy individuals have a constant need for variety, feelings, and new engagements. They set aside everyday and ordinary tasks and seek new experiences. They are adventurous, take risks, and discover new things.
Author: Hamidreza Hasari (Coach)
Mentalland




